What is a bearing? Definition and types of bearings

In this article, we explain what is a bearing, its operation and the different types of bearings used in industry.
What is a mechanical bearing? Definition and industrial role
In the field of mechanics and industry, bearings are essential components that are often inconspicuous but absolutely indispensable to the proper functioning of machines. Found in numerous industrial, automotive, and electromechanical devices, they play a key role in the performance, reliability, and durability of mechanical systems.
Definition of a mechanical bearing
A bearing is a mechanical component designed to guide rotational movement while reducing friction between two moving parts. It supports loads (radial, axial, or combined) while ensuring smooth and precise rotation.
Through the use of rolling elements (balls, rollers, or needles), bearings limit energy loss, reduce component wear, and improve the overall efficiency of machines.
A bearing generally consists of several essential components: an inner ring, an outer ring, rolling elements (balls or rollers), and a cage to maintain their spacing.
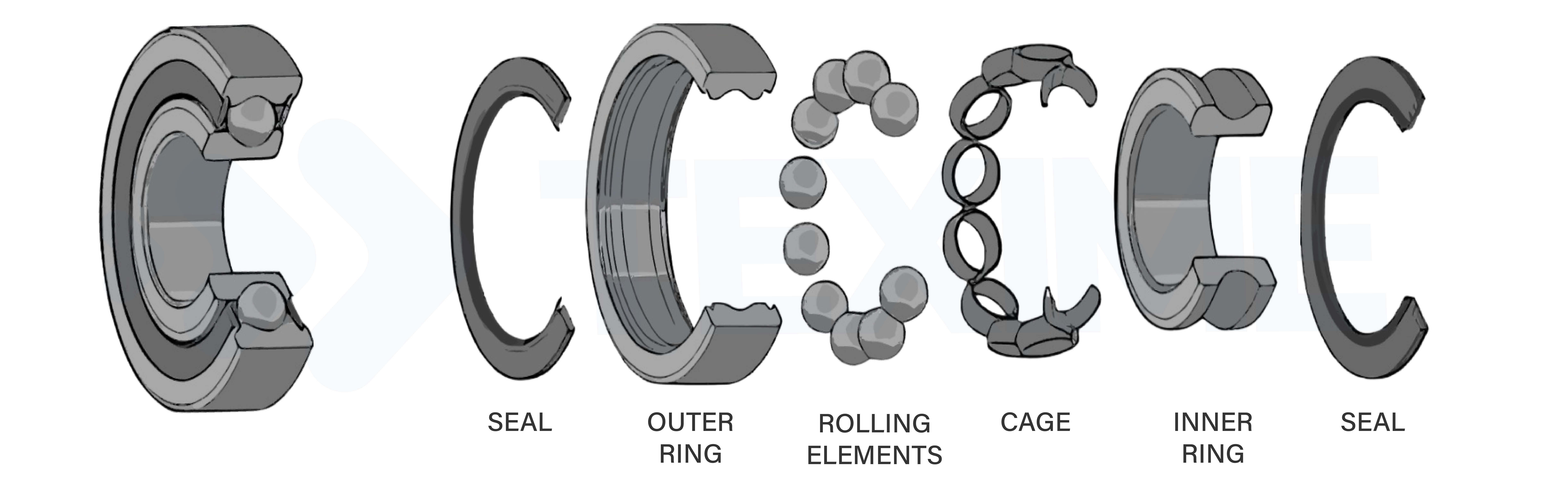
Example of a bearing composition
Non-contractual illustration – the composition of a bearing may vary depending on the model.
► OUTER RING
The outer ring is the part of the bearing that is attached to the bearing housing and does not rotate. It supports the rolling elements on the other side.
It also has a roller track.
► INNER RING
The inner ring is the part of the bearing that is usually mounted on the rotating shaft, rotates with it, and supports the rolling elements. It plays an essential role in transmitting motion and mechanical forces.
It has a raceway (or path), a machined surface on which the rolling elements move.
► ROLLING ELEMENTS
The rolling elements perform the main function of the bearing: enabling rotation with minimal friction. Depending on the application and the loads to be supported, they can take different forms:
- Balls
- Cylindrical rollers
- Conical rollers
- Spherical rollers
- Needles
They circulate on the raceways of the inner and outer rings, distributing loads evenly and improving the load capacity, precision and overall performance of the bearing. They are kept spaced apart and guided by the cage.
► CAGE
The cage serves to maintain a regular spacing between the rolling elements and to guide them during rotation.
Depending on the conditions of use (speed, temperature, environment), the cage can be made from different materials:
- Steel
- Brass
- Polyamide
The cage contributes directly to the reliability, performance and service life of the bearing.
What is a bearing used for?
The main role of a bearing is to:
- Reduce mechanical friction
- Facilitate shaft rotation
- Support heavy loads
- Improve equipment service life
- Limit heating and vibrations
Without bearings, mechanical parts would be subject to excessive friction, leading to rapid wear, excessive energy consumption and frequent breakdowns.
The main types of bearings
There are several subfamilies of bearings, each suited to specific uses:
► Ball bearing
|
Versatile and widely used, ball bearings mainly support radial loads and, to a lesser extent, axial loads. They offer low friction and are suitable for high speeds. Ball bearings use balls as rolling elements. The contact surface between the balls and the raceways is characterised by a point. |
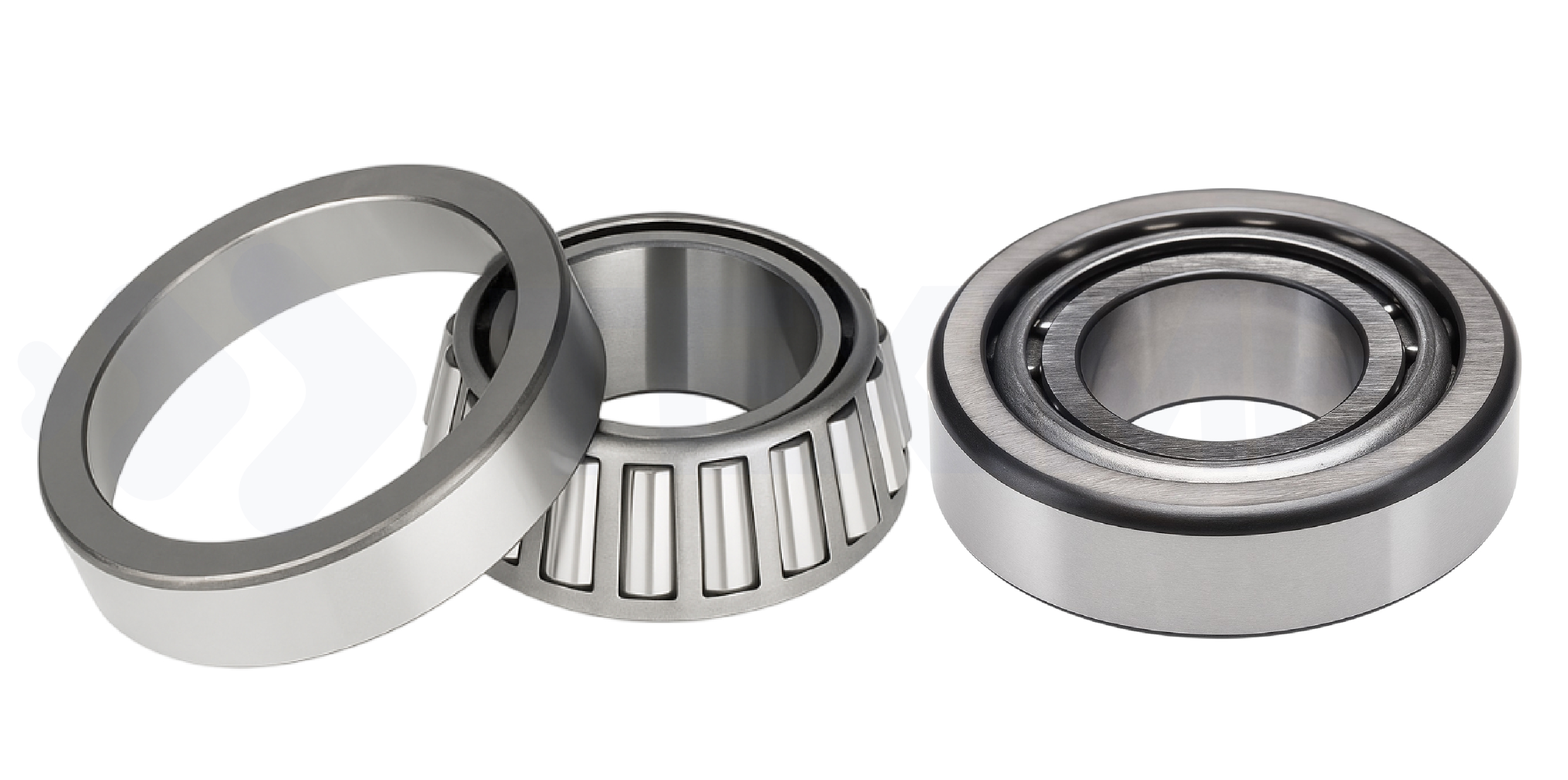
► Tapered roller bearing
|
Designed to support combined loads (radial and axial), they are particularly suitable for applications subject to high stresses, such as transmissions and hubs. Tapered roller bearings consist of raceways on the inner and outer rings. The rolling elements are tapered rollers, which have a wide contact line between the rings and rolling elements. |
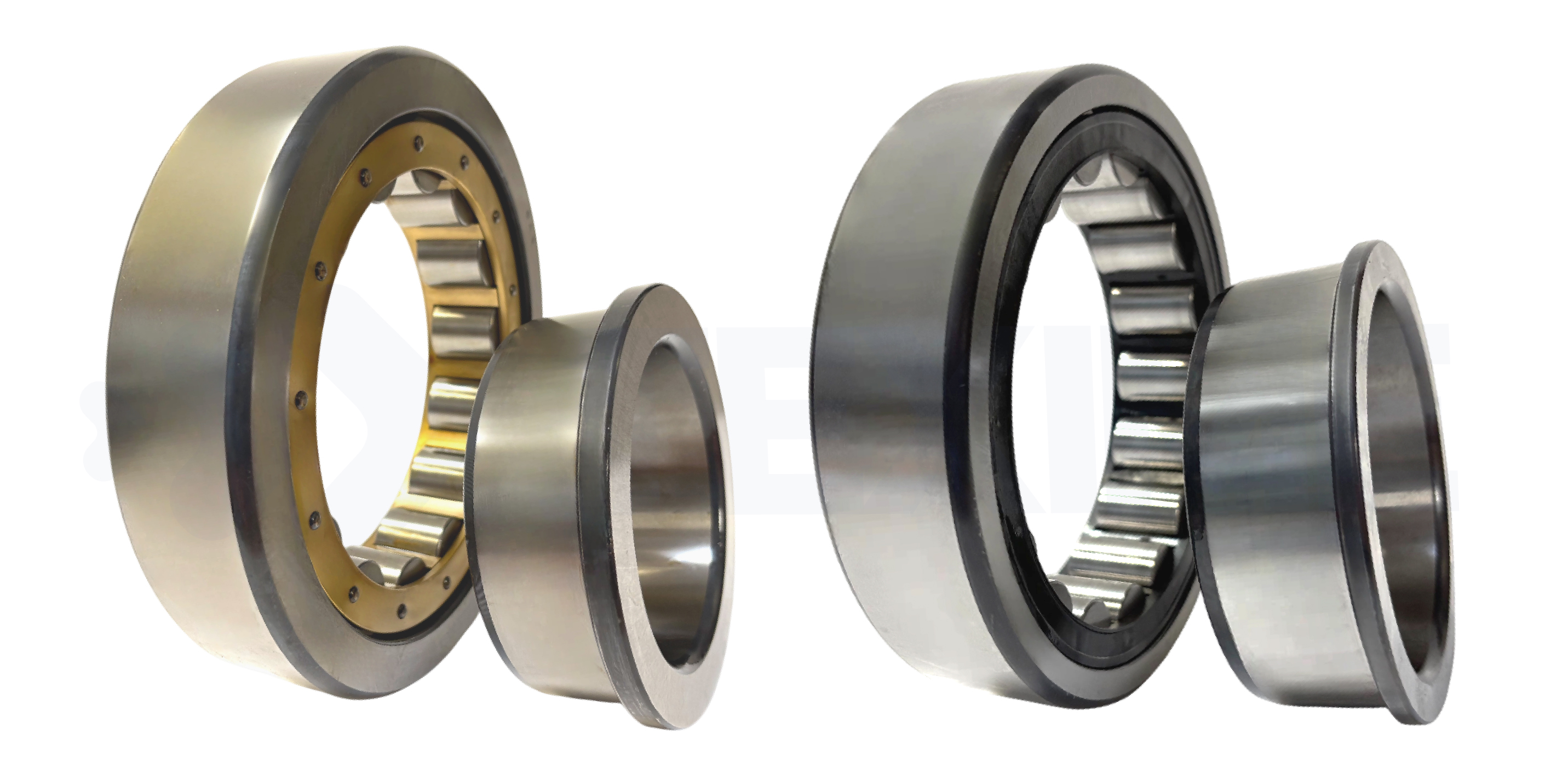
► Cylindrical roller bearing
|
Ideal for high radial loads, these bearings offer high rigidity and excellent mechanical strength, while allowing high rotational speeds. Cylindrical roller bearings are characterised by a line of contact between the rolling elements and the inner/outer rings, which optimises load distribution over a large surface area. |
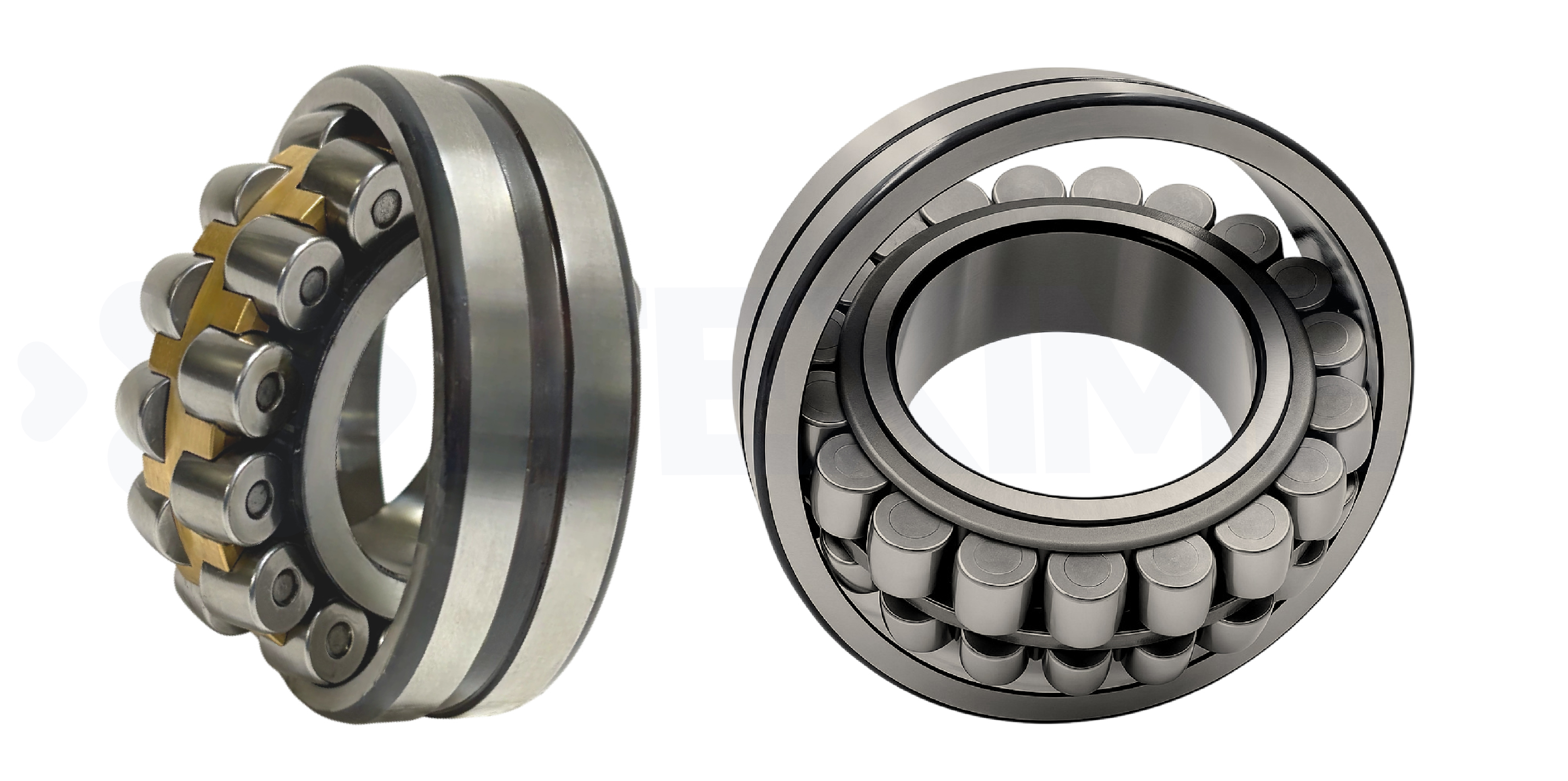
► Spherical roller bearing
|
These spherical roller bearings compensate for misalignments while supporting heavy loads. They are ideally suited to demanding industrial environments and applications subject to vibration. |
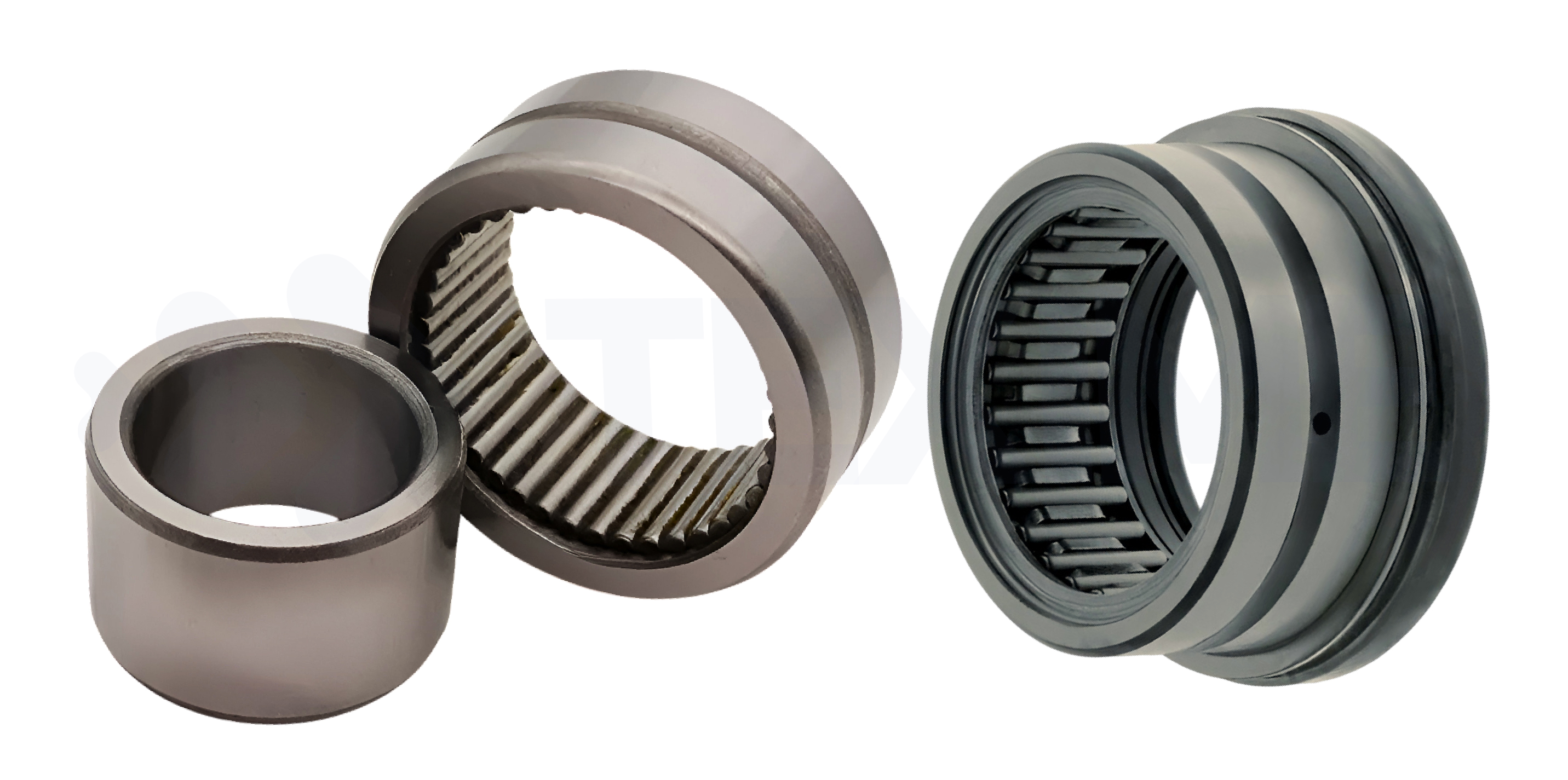
► Needle bearing
|
Compact and lightweight, needle bearings can withstand high radial loads despite their small size. They are used when space is limited. The rolling elements are characterised by their long, thin shape, reminiscent of needles. |
► Thrust bearings
|
The thrust bearings are specially designed to support axial loads only. They are used when the force is exerted in the axis of rotation, with or without radial load depending on the model. |
Where can bearings be found?
Bearings are found in a wide range of equipment, including:
- Electric motors
- Gear motors
- Industrial conveyors
- Machine tools
- Pumps and fans
- Industrial and agricultural vehicles
In industry, a faulty bearing can cause a complete shutdown of a facility, hence the importance of choosing a suitable, high-quality model.
How to choose the right bearing?
The choice of a bearing depends on several technical criteria:
- Load type (radial, axial or combined)
- Rotational speed
- Environment (dust, humidity, temperature)
- Dimensions and tolerances
- Desired service life
A poor choice can lead to premature wear, excessive vibration or costly breakdowns.
For further information, here are the answers to the most frequently asked questions about mechanical bearings.
FAQ – Everything you need to know about bearings
What is a mechanical seal?
A mechanical bearing is a component that guides a rotating part by reducing friction and supporting radial and/or axial loads.
How does a ball bearing work?
A ball bearing uses balls placed between two rings. The balls roll on raceways to limit friction and allow smooth rotation.
What are the different types of bearings?
The main types of bearings are: ball bearings, roller bearings (cylindrical or tapered), needle bearings, spherical roller bearings and thrust bearings.
How to choose the right industrial bearing?
The choice depends on the type of load, rotational speed, environment, dimensions and desired service life. The wrong choice can lead to wear, vibration and breakdowns.
Texime's expertise in industrial bearings
At Texime, we put our expertise at the service of professionals by offering a wide range of industrial bearings, suitable for all sectors of activity. We also support our customers in the diagnosis, replacement and maintenance of their mechanical equipment.
Our objective: to guarantee reliability, performance and longevity for your industrial installations.






